As biomanufacturing continues to scale from lab to production, stability, scalability, and traceability have become central to process optimization. The Multilayer Cell Factory System, once viewed merely as a culture vessel, is now evolving into an integrated, intelligent, and closed platform that anchors modern adherent cell culture processes.
As biomanufacturing continues to scale from lab to production, stability, scalability, and traceability have become central to process optimization. The Multilayer Cell Factory System, once viewed merely as a culture vessel, is now evolving into an integrated, intelligent, and closed platform that anchors modern adherent cell culture processes.
1. From Vessels to Systems: A Shift in Role
Traditionally, cell factories were used for large-scale adherent cell expansion.
Today, they are part of a broader bioprocess framework—integrating with medium bottles, tubing assemblies, and automated filling systems to ensure process consistency and contamination control.
This transformation reflects a key mindset change: the cell factory is no longer a passive container, but an active system component in modern cell-based production lines.
2. Closed Systems: A New Approach to Contamination Control
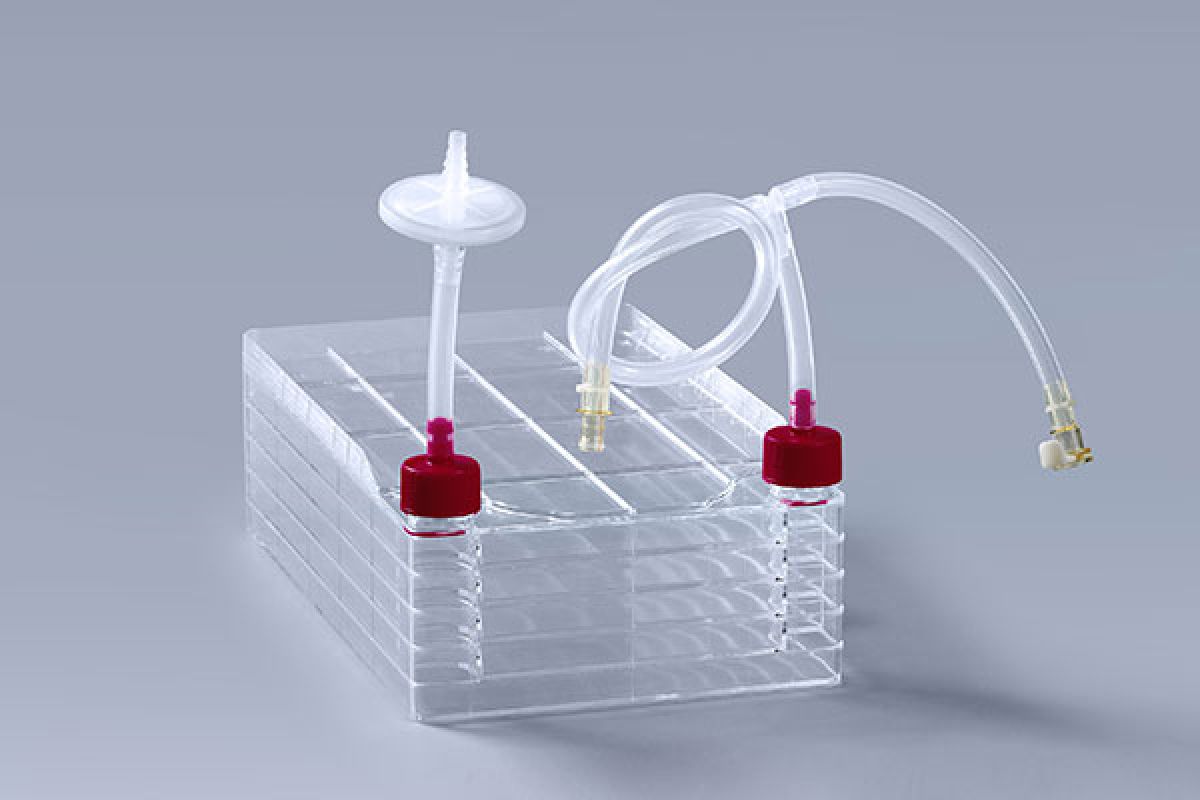
Open handling remains one of the biggest contamination risks in scale-up.
By adopting pre-assembled, Closed System Cell Factory with Tubing, all liquid transfer—including media feeding and waste removal—occurs in a sealed pathway, minimizing operator exposure.
This approach is increasingly used in vaccine manufacturing, viral vector production, and exosome processing, aligning with cGMP standards for aseptic fluid transfer.
3. Intelligent Monitoring and Automated Control
Emerging “smart” cell factory integrate temperature, gas flow, and liquid level sensors for real-time monitoring.
These digital interfaces allow automated control and data recording, paving the way for AI-driven process optimization and electronic batch traceability.
In the near future, such systems could directly interface with automated media exchange units and*continuous culture modules, making industrial-scale adherent culture both efficient and intelligent.
4. Green Manufacturing and Safer Materials
With the rise of sustainability in biomanufacturing, advanced materials such as medical-grade PS and PC ensure optimal cell attachment while reducing extractables.
Manufacturing in energy-efficient ISO Class C cleanrooms, combined with recyclable packaging and quality traceability systems, reflects a broader commitment to ESG and green production.
5. Conclusion: System Thinking for Cell Culture Innovation
The evolution of the cell factory—from container to intelligent closed system—mirrors the modernization of the entire cell culture industry.
As automation and data integration redefine production standards, manufacturers with advanced design, cleanliness, and quality control capabilities will play a leading role in shaping the next generation of scalable cell culture solutions.